Configuring 4G
Users can optionally choose ED-IPC and ED-HMI devices with 4G versions. Before using the 4G network, related configurations are required. If the purchased ED-IPC or ED-HMI device includes 4G functionality, the 4G function is enabled by default from the factory. After inserting the SIM card and powering on the device, the 4G network will connect automatically.
The 4G dial-up reconnection software package (ed-qmi-tool) is pre-installed by default on our company's devices. It is recommended that users utilize this tool to connect to 4G networks. The following section details the specific steps to configure and connect to a 4G network using the pre-installed ed-qmi-tool.
TIP
If users have other requirements and wish to configure the network using the Network Manager tool in Raspberry Pi OS, please refer to Configuring 4G.
Scenarios Without APN Configuration
If the user's 4G network does not require APN configuration, the 4G network status can be checked by following the steps below.
Preparation:
- The ED-IPC or ED-HMI device has started normally.
- A Nano SIM card with 4G network service has been correctly installed into the device's SIM card slot.
NOTE
Please turn off the power before inserting or removing the Nano SIM card.
Steps:
- Open the command window and execute the following command to check if the 4G network is connected.
ifconfig
The returned information is as shown in the figure below (the wwan0 interface indicates the 4G interface):
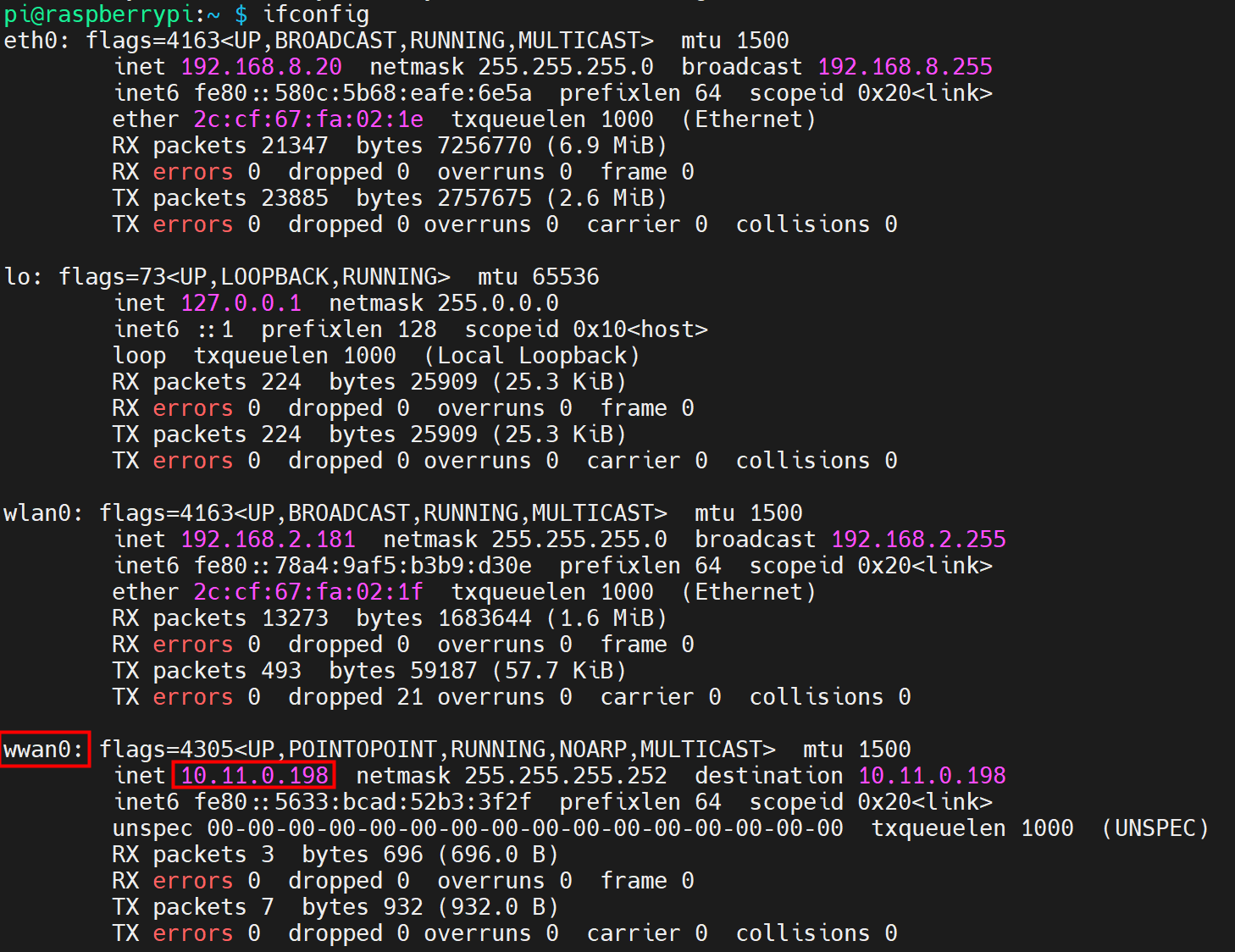
- If the wwan0 interface in the returned information displays a specific IP address, it indicates that the 4G network is connected.
- If the wwan0 interface in the returned information does not display a specific IP address, it indicates that the 4G network is not connected.
- Execute the following command to query the status of the 4G service.
sudo systemctl status ed-lte-daemon.service
The returned information is as shown in the figure below:
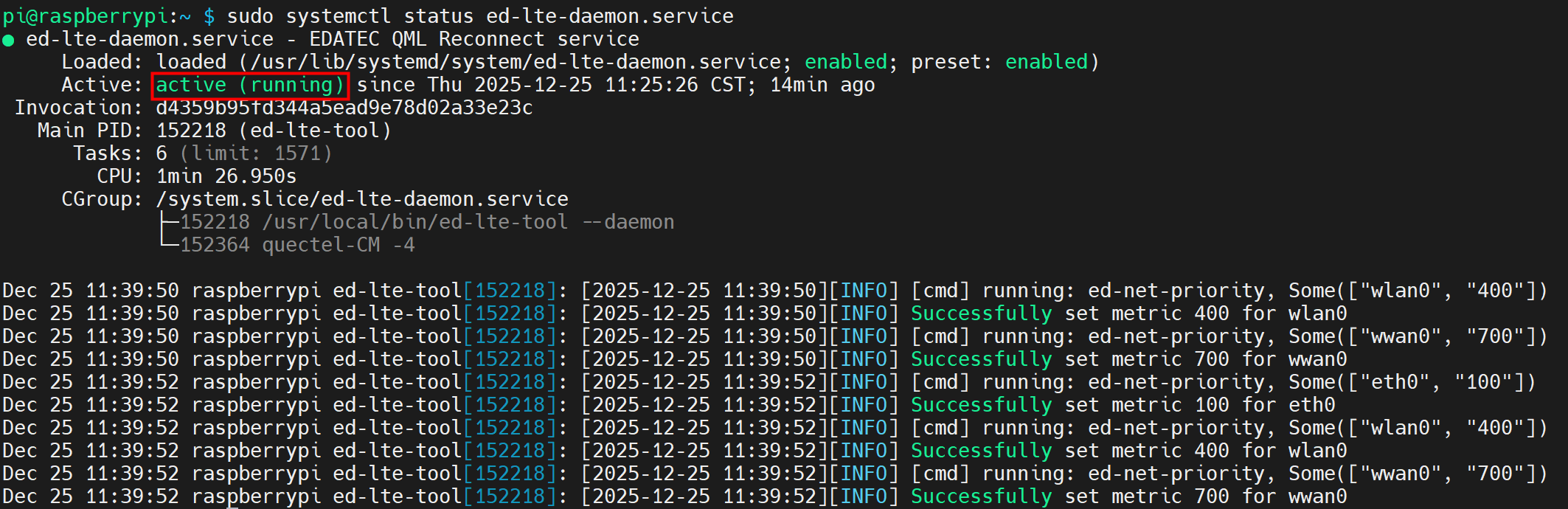
- If the information at the marked position in the returned message shows "Active: active (running)", it indicates that the 4G status is normal.
- If the information at the marked position in the returned message shows "Active: inactive (dead)", it indicates that the 4G status is abnormal.
Scenarios With APN Configuration
If the user's 4G network requires APN configuration, it can be configured by following the steps below.
Preparation:
- The ED-IPC or ED-HMI device has started normally.
- A Nano SIM card with 4G network service has been correctly installed into the ED-IPC or ED-HMI SIM card slot.
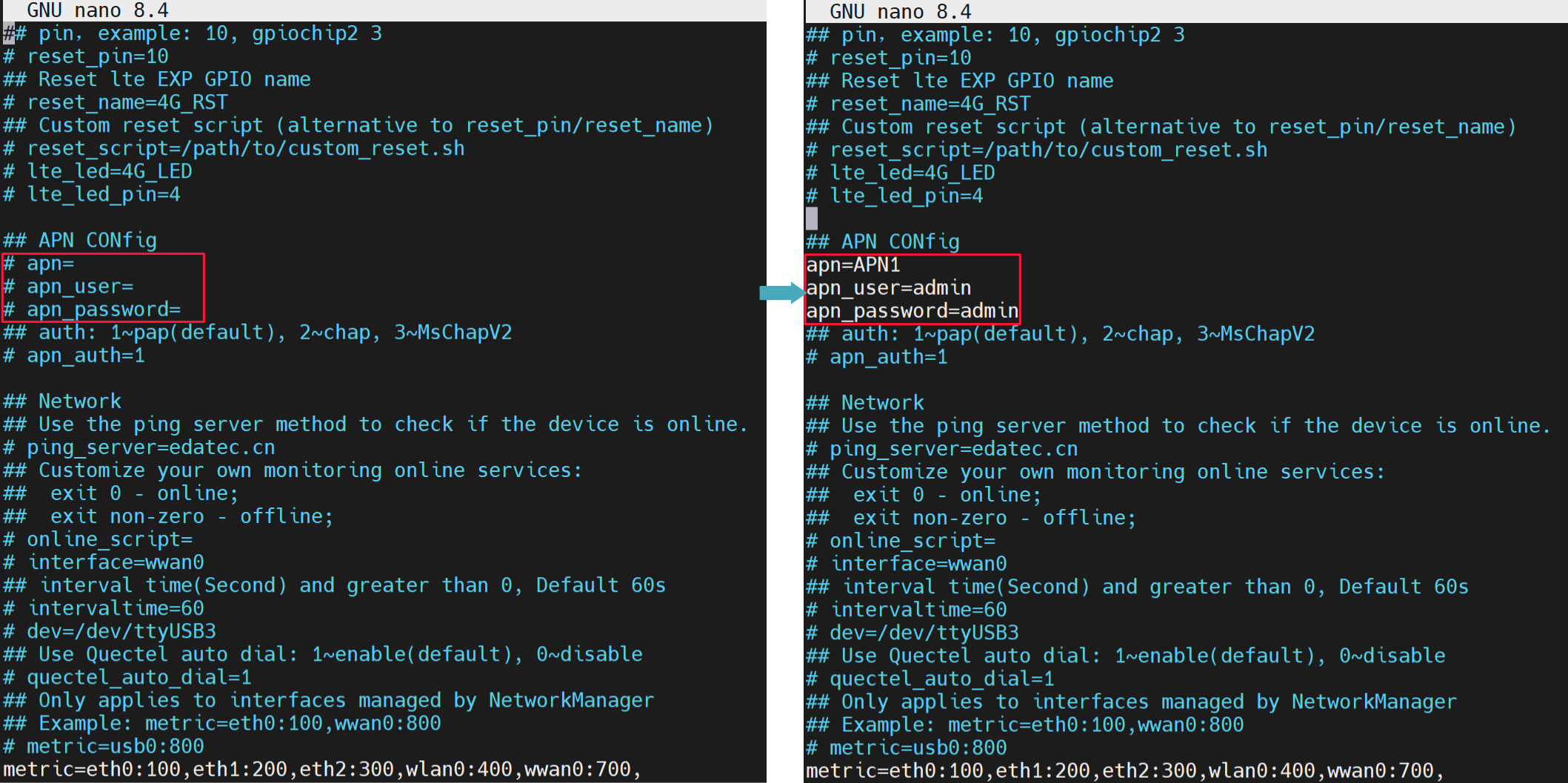
- The APN name, username, and password have been obtained. The following information is used as an example:
- APN name: APN1
- Username: admin
- Password: admin
NOTE
Please turn off the power before inserting or removing the Nano SIM card.
Steps:
- Open the command window and execute the following commands in sequence to open the ed-qml.conf configuration file.
cd /etc/
sudo nano ed-qml.conf
- Configure the "apn", "apn_user", and "apn_password" in the "APN Config" section as needed.
TIP
Parameters such as "4G reset", "Network", and "intervaltime" all support user configuration as needed.
Press
Ctrl+Oto save the file, then pressEnter, and finally pressCtrl+Xto exit the file editing mode.Execute the following command to restart the 4G network service for the configuration to take effect.
sudo systemctl restart ed-lte-daemon.service
- Open the command window and execute the following command to check if the 4G network is connected.
ifconfig
The returned information is as shown in the figure below (the wwan0 interface indicates the 4G interface):

- If the wwan0 interface in the returned information displays a specific IP address, it indicates that the 4G network is connected.
- If the wwan0 interface in the returned information does not display a specific IP address, it indicates that the 4G network is not connected.
- Execute the following command to query the status of the 4G service.
sudo systemctl status ed-lte-daemon.service
The returned information is as shown in the figure below:

- If the information at the marked position in the returned message shows "Active: active (running)", it indicates that the 4G status is normal.
- If the information at the marked position in the returned message shows "Active: inactive (dead)", it indicates that the 4G status is abnormal.
Basic Configuration Commands
If the 4G network cannot be connected, use the following commands for querying and configuration.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| sudo ed-lte-tool --daemon | Start the 4G monitoring program and automatically connect to the 4G network |
| ifconfig | Check if the 4G network is connected. The wwan0 interface represents the 4G interface, as shown in the figure below.
|
| sudo systemctl status ed-lte-daemon.service | Check the service status of 4G, as shown in the figure below.
|
| sudo systemctl enable ed-lte-daemon.service | Enable the 4G service |
| sudo systemctl start ed-lte-daemon.service | Start the 4G service |
| sudo systemctl stop ed-lte-daemon.service | Stop the 4G service |
| sudo ed-lte-tool -m | View 4G module information |
| sudo ed-lte-tool -s | Check 4G signal strength |
| sudo ed-lte -c | Dial-up to connect to the internet |
| sudo ed-lte -d | Disconnect the network connection. Automatic reconnection is not supported after disconnection |
| cd /var/log/ed-qmi/ sudo nano xxxx-xx-xx.log | Enter the /var/log/ed-qmi/ directory to view log files, where xxxx-xx-xx is year-month-day, format like 2025-06-18 |
| journalctl -u ed-lte-daemon.service | View real-time logs of the 4G network |
TIP
When the 4G port connection is normal, if the 4G service status is found to be abnormal, you can execute the following commands in sequence to enable and start the 4G service.
sudo systemctl enable ed-lte-daemon.service
sudo systemctl start ed-lte-daemon.service
