4 Software Operation Guide
4.1 Finding Device IP
4.2 Remote Login
4.3 Configuring Storage Devices
4.4 Configuring Ethernet IP
4.5 Configuring Wi-Fi (Optional)
4.6 Configuring Bluetooth (Optional)
4.7 RTC
The ED-CM4NANO is integrated with RTC. For the version sold in China, we will install CR1220 button cell (RTC backup power supply) by default when shipping. In this way, the system can be guaranteed to have an uninterrupted and reliable clock, which is not affected by factors such as equipment power down.
The default shipping system image will integrate the RTC automatic synchronization service we wrote, so guests can automatically synchronize the clock without setting it, and can use RTC without feeling. The general principle is:
- When the system is turned on, the service automatically reads the saved time from RTC and synchronizes it to the system time.
- If there is an Internet connection, the system will automatically synchronize the time from the NTP server and update the local system time with Internet time.
- When the system is shut down, the service automatically writes the system time into RTC and updates the RTC time.
- Because of the installation of button cell, although the CM4 Nano is powered off, the RTC is still working and timing.
In this way, we can ensure that our time is accurate and reliable.
TIP
If it is the first time to boot, because there is no effective time in RTC, synchronization may fail, so just restart it directly. When rebooting, the system time will be written into RTC for normal use.
If you don't want to use this service, you can turn it off manually:
sudo systemctl disable rtc
sudo reboot
Re-enable this service:
sudo systemctl enable rtc
sudo reboot
Read RTC Time manually:
sudo hwclock -r
2022-11-09 07:07:30.478488+00:00
Manually synchronize RTC time to the system:
sudo hwclock -s
Write the system time into RTC:
sudo hwclock -w
4.8 Buzzer
The buzzer is controlled by GPIO6.
- open the buzzer:
raspi-gpio set 6 op dh
- close the buzzer:
raspi-gpio set 6 op dl
4.9 Serial Communication
4.9.1 Install The picocom Tool
Picocom serial terminal can be debugged conveniently in Linux environment.
- Execute the following command to install picocom.
sudo apt-get install picocom
Execute the following commands as applicable:
- input
Ctrl+afirst, and thenCtrl+hto see the available commands.
*** Picocom commands (all prefixed by [C-a])
*** [C-x] : Exit picocom
*** [C-q] : Exit without reseting serial port
*** [C-b] : Set baudrate
*** [C-u] : Increase baudrate (baud-up)
*** [C-d] : Decrease baudrate (baud-down)
*** [C-i] : Change number of databits
*** [C-j] : Change number of stopbits
*** [C-f] : Change flow-control mode
*** [C-y] : Change parity mode
*** [C-p] : Pulse DTR
*** [C-t] : Toggle DTR
*** [C-g] : Toggle RTS
*** [C-|] : Send break
*** [C-c] : Toggle local echo
*** [C-w] : Write hex
*** [C-s] : Send file
*** [C-r] : Receive file
*** [C-v] : Show port settings
*** [C-h] : Show this message- input
Ctrl+afirst, thenCtrl+cto switch the local echo mode. - input
Ctrl+afirst, thenCtrl+qto exit picocom.
- input
4.9.2 Debug UART
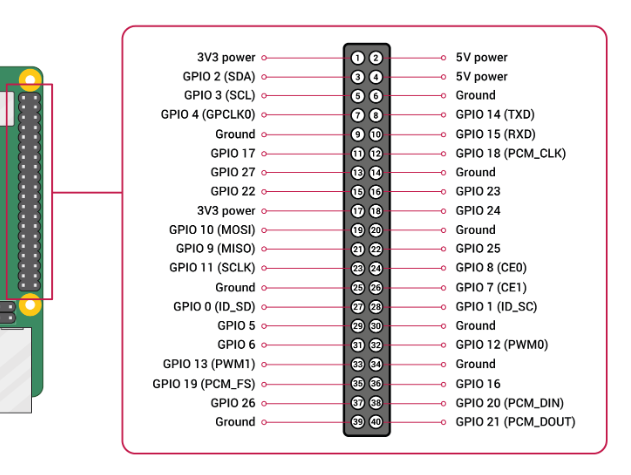
The 40-PIN header on ED-CM4NANO includes a debug serial port (GPIO14 = RX, GPIO15 = TX). Enable it via these steps.
- Execute the following command to launch raspi-config.
sudo raspi-config
- choose option 3 - Interface Options.
- choose option P6 - Serial Port.
- When prompted Would you like a login shell to be accessible over serial?, answer Yes.
- Exit raspi-config
- Execute the following command to restart device.
sudo reboot
- Edit
config.txtand addenable_uart=1at the end.
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
TIP
The default baud rate for the debug serial port is 115200. To verify the current baud rate, inspect cmdline.txt.
sudo nano /boot/cmdline.txt
