Configuring Serial Port Parity Bits
1 Overview
Introduces the background and scope of configuring serial port parity bits.
1.1 Background
The serial port parity bit (Parity) is used to detect errors in data transmission. Common parity modes are odd parity, even parity, and no parity. Some customers, when using the serial port function of ED-IPC1100, need to configure the serial port parity bit to achieve reliable data transmission. To address this requirement, our company provides detailed operating instructions to help users correctly configure the serial port parity bit.
1.2 Scope of Application
This application applies to the ED-IPC1100 device.
2 Application Guide
The following uses the RS485 of the ED-IPC1100 device as an example to introduce the operation steps for installing and configuring the serial port parity bit.
2.1 Serial Port Mapping
Before installation, please confirm the device's serial port mapping and Bluetooth overlay settings to ensure /dev/serial0 points to the expected hardware device /dev/ttyAMA0.
Preparation:
- The ED-IPC1100 has started normally and is connected to the network.
Steps:
- Open a command window and execute the following command to open the
config.txtfile.
sudo nano /boot/firmware/config.txt
- Configure the
dtoverlayparameter as needed.
- Configure as
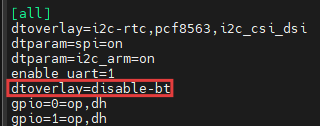
dtoverlay=disable-bt, as shown in the figure below. This setting means/dev/serial0points to the hardware port/dev/ttyAMA0(/dev/serial0-> ttyAMA0), disables Bluetooth, and the PL011 (hardware UART) is used for the serial port (recommended for stable communication).
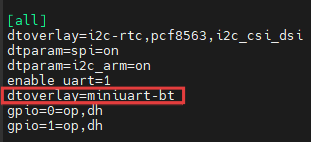
-Configure as dtoverlay=miniuart-bt, as shown in the figure below. This setting means /dev/serial0 points to the hardware port /dev/ttyAMA0 (/dev/serial0-> ttyAMA0), retains Bluetooth but uses the mini UART, the PL011 (hardware UART) is used for the serial port, and the baud rate may be affected by CPU frequency (carries a risk of instability).
Press
Ctrl+Oto save the file, then pressEnter, and finally pressCtrl+Xto exit file editing mode.Execute the following command to restart the device for the configuration to take effect.
sudo reboot
- Execute the following command to verify the mapping.
readlink -f /dev/serial0
2.2 Configuring the Serial Port Parity Setting Service
Preparation:
- The ED-IPC1100 has started normally and is connected to the network.
Steps:
- Open a command window and execute the following command to create the installation file.
sudo nano serial-service-installer.sh
- Copy the following script content into the file:
#!/bin/bash
set -e
SCRIPT_NAME="serial-service-installer.sh"
SERVICE_NAME="serial-parity.service"
INSTALL_PATH="/usr/local/bin/serial-parity-daemon"
SERVICE_FILE="/etc/systemd/system/$SERVICE_NAME"
CONFIG_FILE="/etc/serial-parity.conf"
# Default configuration
SERIAL_PORT="/dev/ttyAMA0"
BAUD_RATE="9600"
PARITY_MODE="even"
log() {
echo "[INFO] $(date '+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') - $1"
}
warn() {
echo "[WARN] $(date '+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') - $1"
}
error() {
echo "[ERROR] $(date '+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') - $1"
}
manage_config() {
local action="$1"
local file_path="$2"
case "$action" in
"ensure")
if [ ! -f "$file_path" ]; then
mkdir -p "$(dirname "$file_path")" 2>/dev/null || true
cat > "$file_path" << 'EOF'
# Serial Port Parity Configuration
# even parity|odd parity|no parity
PARITY_MODE=even
# Interface configuration
SERIAL_PORT=/dev/ttyAMA0
# Baud rate configuration
BAUD_RATE=9600
EOF
chmod 644 "$file_path" 2>/dev/null || true
log "Created configuration file: $file_path"
fi
;;
"load")
if [ -f "$file_path" ]; then
source "$file_path"
fi
;;
esac
}
check_root() {
if [[ $EUID -ne 0 ]]; then
error "This operation requires root privileges. Please execute with sudo."
exit 1
fi
}
check_serial_device() {
local device="$1"
if [ ! -e "$device" ]; then
warn "Serial device $device does not exist, but proceeding with installation."
return 1
fi
if [ ! -r "$device" ] || [ ! -w "$device" ]; then
warn "Insufficient permissions for serial device $device"
return 1
fi
log "Serial device $device check passed."
return 0
}
create_daemon_script() {
local daemon_path="$1"
log "Creating main service program..."
cat > "$daemon_path" << 'DAEMON_EOF'
#!/bin/bash
# Serial Port Parity Daemon
CONFIG_FILE="/etc/serial-parity.conf"
log() {
echo "$(date '+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') - $1"
}
apply_serial_settings() {
(
case "$PARITY_MODE" in
"even")
stty -F "$SERIAL_PORT" speed "$BAUD_RATE" cs7 parenb -parodd -cstopb
;;
"odd")
stty -F "$SERIAL_PORT" speed "$BAUD_RATE" cs7 parenb parodd -cstopb
;;
*)
stty -F "$SERIAL_PORT" speed "$BAUD_RATE" cs8 -parenb -cstopb
;;
esac
) >/dev/null 2>&1
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
log "Serial settings applied successfully: mode=$PARITY_MODE, baud rate=$BAUD_RATE"
return 0
else
log "Failed to apply serial settings"
return 1
fi
}
set_config() {
local new_value="$1"
[ -f "$CONFIG_FILE" ] && source "$CONFIG_FILE"
case "$new_value" in
"even"|"odd"|"none")
sed -i "s/^PARITY_MODE=.*/PARITY_MODE=$new_value/" "$CONFIG_FILE"
PARITY_MODE="$new_value"
log "Set parity mode: $PARITY_MODE"
;;
*)
if [[ "$new_value" =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]] && [ "$new_value" -ge 300 ] && [ "$new_value" -le 4000000 ]; then
sed -i "s/^BAUD_RATE=.*/BAUD_RATE=$new_value/" "$CONFIG_FILE"
BAUD_RATE="$new_value"
log "Set baud rate: $BAUD_RATE"
else
echo "Error: Invalid parameter '$new_value'"
echo "Usage: $0 set {even|odd|none|baud_rate}"
return 1
fi
;;
esac
apply_serial_settings
}
show_help() {
cat <<'EOF'
Serial Port Parity Service
Usage: /usr/local/bin/serial-parity-daemon set {none|odd|even|baud_rate}
Setting examples:
sudo serial-parity-daemon set odd # Odd parity
sudo serial-parity-daemon set 115200 # 115200 baud rate
Service management:
sudo systemctl {start|stop|status} serial-parity.service
EOF
}
main_service() {
[ -f "$CONFIG_FILE" ] && source "$CONFIG_FILE"
log "Starting serial service: $SERIAL_PORT, $BAUD_RATE, $PARITY_MODE"
[ ! -e "$SERIAL_PORT" ] && {
log "Error: Serial device does not exist"
exit 1
}
apply_serial_settings || exit 1
log "Service running"
while true; do
sleep 3600
done
}
case "${1:-}" in
"start") main_service ;;
"set")
[ -n "$2" ] && set_config "$2" || {
echo "Usage: $0 set {even|odd|none|baud_rate}"
exit 1
}
;;
"help"|"-h"|*) show_help ;;
esac
DAEMON_EOF
chmod +x "$daemon_path"
log "Main service program created: $daemon_path"
}
create_systemd_service() {
log "Creating systemd service file..."
cat > "$SERVICE_FILE" << SERVICE_EOF
[Unit]
Description=Serial Port Parity Configuration Service
After=multi-user.target
[Service]
Type=simple
ExecStart=$INSTALL_PATH start
Restart=always
RestartSec=5
User=root
Group=dialout
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
SERVICE_EOF
log "Systemd service file created: $SERVICE_FILE"
}
install_service() {
check_root
log "Starting installation of serial service..."
check_serial_device "$SERIAL_PORT"
mkdir -p "$(dirname "$INSTALL_PATH")"
[ -f "$INSTALL_PATH" ] && {
backup="$INSTALL_PATH.backup.$(date +%Y%m%d_%H%M%S)"
cp "$INSTALL_PATH" "$backup"
log "Existing file backed up: $backup"
}
create_daemon_script "$INSTALL_PATH"
create_systemd_service
manage_config "ensure" "$CONFIG_FILE"
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable "$SERVICE_NAME"
log "Service installation complete."
}
start_service() {
check_root
systemctl start "$SERVICE_NAME" && log "Service started successfully." || {
error "Failed to start service"
exit 1
}
}
self_cleanup() {
log "Installation complete, cleaning up installation script..."
cat > /tmp/cleanup-$$.sh << 'CLEANUP_EOF'
#!/bin/bash
sleep 3
[ -f "$1" ] && rm -f "$1"
rm -f "$0"
CLEANUP_EOF
chmod +x /tmp/cleanup-$$.sh
nohup /tmp/cleanup-$$.sh "$0" >/dev/null 2>&1 &
}
show_help() {
cat <<'EOF'
Serial Service Installer Script
Usage: sudo ./serial-service-installer.sh install
EOF
}
main() {
case "${1:-}" in
"install")
install_service
start_service
self_cleanup
;;
*) show_help ;;
esac
}
[[ "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}" == "${0}" ]] && main "$@"
- Execute the following commands in sequence to install the script and generate the unit.
sudo chmod +x serial-service-installer.sh
sudo ./serial-service-installer.sh install
- Execute the following command to view the service status.
sudo systemctl status serial-parity.service
2.3 Modifying Serial Port Configuration
Preparation:
- The ED-IPC1100 has started normally and is connected to the network.
Steps:
- Open a command window and execute the following command to open the configuration file.
sudo nano /etc/serial-parity.conf
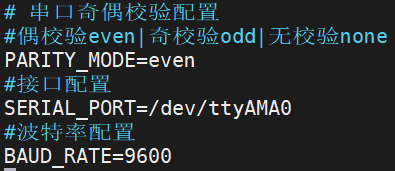
- Modify the parity bit and baud rate as needed.
- even/odd: Typically configured with 7 data bits (cs7);
- none: Use 8 data bits (cs8).
Press
Ctrl+Oto save the file, then press Enter, and finally pressCtrl+Xto exit file editing mode.Execute the following commands in sequence to restart the service for the configuration to take effect.
sudo systemctl stop serial-parity.service
sudo systemctl start serial-parity.service
2.4 Common Operations
- Start the service:
sudo systemctl start serial-parity.service - Stop the service:
sudo systemctl stop serial-parity.service - Enable auto-start on boot:
sudo systemctl enable serial-parity.service - Disable auto-start on boot:
sudo systemctl disable serial-parity.service - Check status:
sudo systemctl status serial-parity.service
